宫内特定期DEHP暴露的远期神经效应及胎脑甲状腺素信号系统扰动机制
人群研究证据提示,孕期塑化剂DEHP暴露将给后代神经发育带来风险,但这种风险的特征,如暴露敏感期和损害的持久性,皆不清楚。
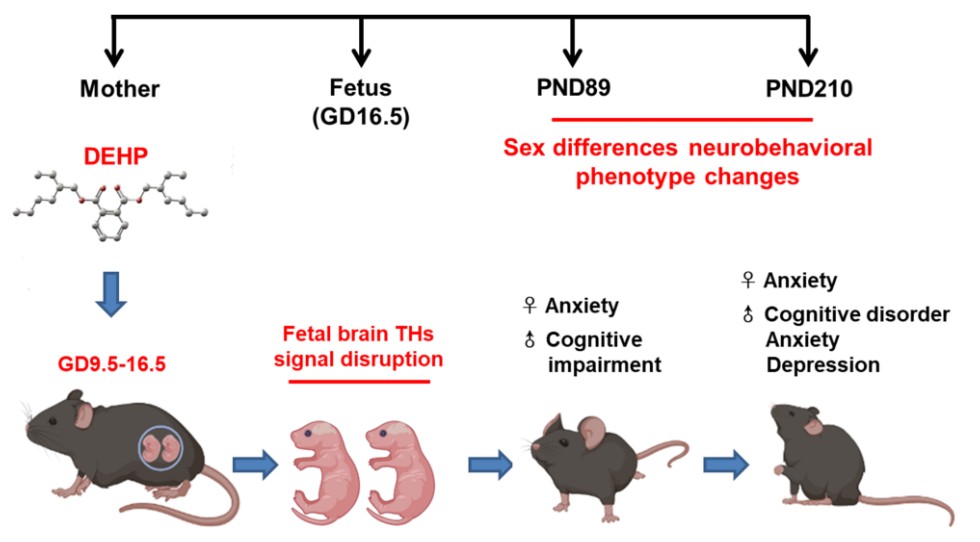
近期,本实验室在《Food and Chemistry Toxicology》(IF:6.023)杂志上发表题为“Maternal exposure to bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate during the thyroid hormone-dependent stage induces persistent emotional and cognitive impairment in middle-aged offspring mice”的研究论文。研究选择在胚胎神经管闭合的孕第9.5天(GD9.5,)至胎鼠自身开始合成甲状腺素(THs)的GD16.5期间,经口灌胃对孕鼠予以DEHP处理。发现孕期DEHP暴露会导致后代小鼠在成年期和中年期出现焦虑、抑郁和认知障碍等神经行为异常,且存在性别差异。进一步研究发现,胎鼠脑中FTHs、TH转运蛋白和脱碘酶 D2(活化T4为T3)显著减少,而脱碘酶D3(T3失活酶)明显升高。同时发现,TH信号下游靶点BDNF的表达明显下调(mRNA和蛋白水平)。提示宫内DEHP暴露可能通过损害胎脑TH信号系统导致子代小鼠长期不可逆的脑损伤以及性别差异性神经发育障碍。
已发表论文:
Lv, J., Li, Y., Chen, J., Li, R., Bao, C., Ding, Z., Ren, W., Du, Z., Wang, S., Huang, Y., & Wang, Q. N. (2022). Maternal exposure to bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate during the thyroid hormone-dependent stage induces persistent emotional and cognitive impairment in middle-aged offspring mice. Food and chemical toxicology : an international journal published for the British Industrial Biological Research Association, 163, 112967. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2022.112967
第一作者:吕佳、李艳玲 通讯作者:黄以超、王取南
撰写人:吕佳
